Neonicotinoid pesticides are detrimental to not only monarch health, but all pollinator health. If you have never heard of Neonicotinoids, or Neonics for short, and aren’t sure why you should care, I urge you to keep reading.
What are Neonicotinoids?
Neonics are a type of pesticide that attacks insects on a neurological level. This means “the way they work is by permanently binding to the nerve cells of insects, overstimulating and destroying them. Exposed insects often exhibit uncontrollable shaking and twitching followed by paralysis before eventually dying” (Lindwall, 2022). These pesticides are used in a variety of ways including on agricultural land, golf courses, lawns, gardens, and even in tick and flea repellents for our pets, making Neonics the most used pesticide in the USA since its development in the 1990s (Lindwall, 2022). I know how they affect insects and I’m not sure I’d want my little furballs anywhere near it.
Why should we care?
Neonics are also extremely harmful to pollinators. They are non-selective, which means that all insects are affected by them. “Since their introduction, neonics have made U.S. agriculture nearly 50 times more harmful to insect life” (Lindwall, 2022). “Almost 45% of the 3374 articles on neonicotinoids published to date … addressed the issue of negative interactions of neonicotinoids with bees and other pollinators” (Jactel et al., 2019). There are so many articles on the internet that address neonics and call for a change in pesticide use. During a 17 year study on butterflies and neonics, it was found that the diversity of butterflies and abundance were negatively affected and declined (Van Deynze et al., 2024). It is thought that these pesticides may have triggered the decline of butterflies in 2003, when treated soybeans became available in the Midwest (Van Deynze et al., 2024). Butterflies aren’t the only pollinator affected by this nasty pesticide. Beekeepers have reported that more than 45% of their honeybee colonies have been lost between 2020 and 2021; this is the second highest colony collapse rate on record (Lindwall, 2022). That’s not all, Iowa is the home of over 4,000 native bee species including the already endangered Rusty Patched bumblebee. This means that all pollinators are at risk due to these chemicals.
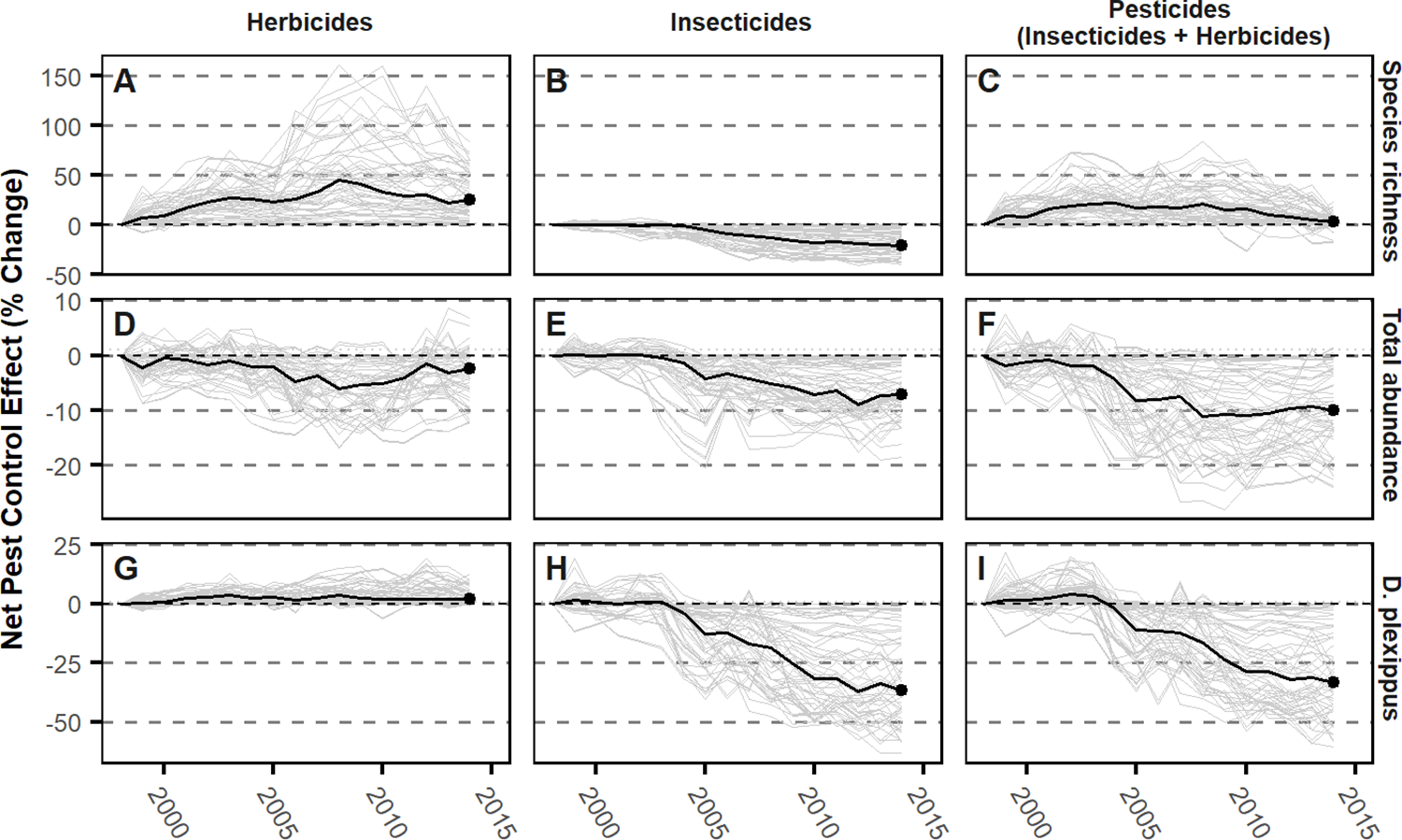
This graph from Van Deynze et al. shows the correlations between pesticide use and the decline in monarch butterfly (D. plexippus) populations throughout the years.
So maybe you don’t care about some bugs. Well, it’s affecting people too. When applied to the soil around a plant, only about 2% – 5% actually get on the target plant, with the rest becoming residue on the soil outside of the plant’s root system’s reach. This residual pesticide then gets washed away by irrigation or rain into our waterways. These are areas we let our children swim and play in. These are areas we are fishing in. These are areas we live by and see daily. A 2015 study by the U.S. Geological Survey found neonic pollution in more than half of the streams it sampled nationwide (Lindwall, 2022).
Don’t worry, we can still do something to help!
Citations
Jactel H, Verheggen F, Thiéry D, Escobar-Gutiérrez AJ, Gachet E, Desneux N, (2019, August). Alternatives to neonicotinoids. Science Direct. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0160412019302351?via%3Dihub
Lindwall, C. (2022, May). Neonicotinoids 101: The effects on humans and bees. NRCD. https://www.nrdc.org/stories/neonicotinoids-101-effects-humans-and-bees
Van Deynze B, Swinton SM, Hennessy DA, Haddad NM, Ries L (2024, June) Insecticides, more than herbicides, land use, and climate, are associated with declines in butterfly species richness and abundance in the American Midwest. PLoS ONE 19(6): e0304319. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0304319